Cinnamon, a beloved spice with a rich history spanning centuries, continues to captivate attention for its diverse culinary uses, medicinal properties, and cultural significance. As we progress into the future, several emerging trends are shaping the trajectory of cinnamon production, consumption, and research.

This comprehensive review explores the future trends of cinnamon, focusing on innovation in cultivation and processing techniques, sustainability practices, health applications, and market dynamics. By examining these trends, we aim to provide insights into the evolving landscape of cinnamon and its potential impact on various sectors, including agriculture, healthcare, and food industries.
Importance of Cinnamon in Modern Cuisine, Medicine, and Cultural
Cinnamon holds profound importance in modern cuisine, medicine, and cultural practices, serving as more than just a spice. It adds depth, warmth, and complexity to a wide array of dishes, from sweet desserts to savory curries. Its versatility extends to beverages, baked goods, and even savory meats, enriching flavors and aromas across global cuisines.
In medicine, cinnamon’s health benefits have garnered increasing attention. Research suggests its potential in managing blood sugar levels, reducing inflammation, and combating oxidative stress. It’s utilized in traditional medicine systems worldwide for various ailments, showcasing its medicinal versatility and cultural significance.
Culturally, cinnamon has deep-rooted associations, symbolizing warmth, hospitality, and celebration. It’s intertwined with rituals, ceremonies, and festive occasions in many cultures, enriching traditions with its aromatic presence.
Overall, cinnamon’s significance transcends mere flavoring; it embodies a blend of culinary artistry, therapeutic potential, and cultural heritage, making it an indispensable component of modern lifestyles around the globe.
Innovations in Food and Beverage
Cinnamon, with its warm, aromatic flavor, has been a staple spice in culinary traditions worldwide for centuries. In recent years, there have been several innovative uses of cinnamon in the food and beverage industry.
- Cinnamon Infusions: Beyond traditional cinnamon sticks, chefs and mixologists are infusing cinnamon into oils, syrups, and spirits to impart its unique flavor profile into dishes and cocktails. Cinnamon-infused vodka, rum, and even tequila have gained popularity for their rich, spiced undertones.
- Cinnamon Blends: Food companies are incorporating cinnamon into unique spice blends, offering consumers convenient ways to add depth to their cooking. These blends often combine cinnamon with complementary spices like nutmeg, cloves, and cardamom, enhancing both sweet and savory dishes.
- Cinnamon in Desserts: Pastry chefs are experimenting with cinnamon in desserts beyond the classic cinnamon roll. Cinnamon is being used in ice creams, chocolates, and baked goods like cakes and cookies, adding warmth and complexity to sweet treats.
- Cinnamon Beverages: Coffee shops and breweries are incorporating cinnamon into their beverage offerings. Cinnamon lattes, ciders, and even cinnamon-spiced beers are gaining traction for their comforting and flavorful profiles.
- Functional Food Innovations: With growing interest in functional foods, cinnamon is being explored for its potential health benefits. Products like cinnamon-infused energy bars, teas, and supplements are emerging, capitalizing on cinnamon’s reputed antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.
These innovations showcase cinnamon’s versatility and its ability to elevate both traditional and contemporary culinary experiences. As consumer tastes evolve, cinnamon continues to inspire creativity in the food and beverage industry.

Technological Advancements in Extraction and Processing
Technological advancements in the extraction and processing of cinnamon have led to more efficient methods for harnessing its flavor and health-promoting compounds. One notable innovation is the utilization of supercritical fluid extraction (SFE) for cinnamon extraction. SFE involves using carbon dioxide (CO2) at a supercritical state as a solvent to extract cinnamon’s bioactive compounds, such as cinnamaldehyde and cinnamic acid. This method offers advantages over traditional solvent extraction techniques, including higher selectivity, reduced solvent usage, and minimal residue in the final product.
Additionally, advancements in ultrasound-assisted extraction (UAE) and microwave-assisted extraction (MAE) have been applied to cinnamon processing. UAE and MAE utilize ultrasonic waves and microwave energy, respectively, to enhance the extraction efficiency of cinnamon’s phytochemicals. These techniques facilitate faster extraction rates, increased yields, and preservation of heat-sensitive compounds, resulting in higher-quality cinnamon extracts.
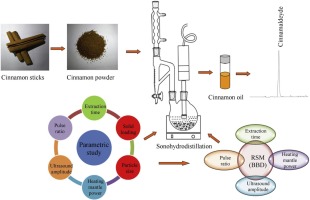
Moreover, advancements in nanotechnology have been incorporated into cinnamon extraction processes. Nanoparticles are used to improve the surface area available for interaction between cinnamon and solvents, leading to enhanced extraction efficiency and improved product quality.
Overall, these technological advancements in extraction and processing are driving innovation in the cinnamon industry, enabling the production of high-quality cinnamon extracts with optimized flavor profiles and enhanced health benefits.
Cinnamon Herbal Remedies
Cinnamon has a long history of use in traditional herbal medicine due to its numerous potential health benefits. Some of the most notable herbal remedies associated with cinnamon include:
- Blood Sugar Regulation: Cinnamon is believed to help regulate blood sugar levels by improving insulin sensitivity and reducing insulin resistance. This makes it a popular remedy for managing diabetes and pre-diabetes.
- Antioxidant Properties: Cinnamon is rich in polyphenols, compounds with potent antioxidant properties. These antioxidants help combat oxidative stress in the body, which can contribute to various chronic diseases and aging.
- Anti-inflammatory Effects: Cinnamon contains compounds that possess anti-inflammatory properties. Regular consumption of cinnamon may help reduce inflammation in the body, potentially lowering the risk of inflammatory conditions such as arthritis and certain types of cancer.
- Antimicrobial Activity: Cinnamon has natural antimicrobial properties, which can help fight bacterial, fungal, and viral infections. It has been traditionally used to treat respiratory infections, digestive issues, and skin conditions.
- Heart Health Support: Some research suggests that cinnamon may help improve heart health by lowering cholesterol levels, reducing blood pressure, and promoting healthy blood circulation. These effects may contribute to a reduced risk of cardiovascular diseases.
- Digestive Aid: Cinnamon has been used to aid digestion and relieve gastrointestinal discomfort. It may help reduce gas, bloating, and indigestion, as well as improve overall gut health.
- Cognitive Function: Preliminary studies suggest that cinnamon may have neuroprotective effects and could potentially help improve cognitive function and memory.

It’s important to note that while cinnamon shows promise as an herbal remedy for various health conditions, more research is needed to fully understand its mechanisms of action and potential therapeutic applications.
As with any herbal remedy, it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before using cinnamon for medicinal purposes, especially if you have any underlying health conditions or are taking medications.
Cinnamon Household and Cleaning Products
Cinnamon is also finding its way into household and cleaning products due to its pleasant scent and potential antimicrobial properties. Cinnamon essential oil is often used in natural cleaning solutions for its ability to disinfect surfaces and freshen the air. Additionally, cinnamon-scented candles and air fresheners are popular choices for creating a cozy and inviting atmosphere in homes.

Some laundry detergents and fabric softeners incorporate cinnamon fragrance to impart a warm, comforting scent to clothes and linens. Overall, cinnamon’s aromatic qualities make it a versatile ingredient in various household and cleaning products.
Conclusion
Cinnamon continues to evolve from a kitchen staple to a versatile ingredient with diverse applications, its future appears promising and dynamic. From revolutionizing the food and beverage industry to pioneering innovations in health and wellness, cinnamon’s journey is marked by a blend of tradition and innovation.
Embracing sustainability, quality, and innovation will be key in unlocking the full potential of cinnamon, ensuring its enduring relevance in the ever-changing landscape of consumer preferences and global markets.
